Peripheral Artery Disease Month: Awareness,Prevention, and Living Well
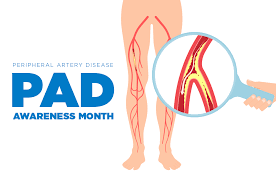
September marks Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) Month, a vital time to spotlight this often-overlooked
condition that affects millions. Approximately twenty percent of people with risk factors have this disease, and
many are not aware of it. As we draw attention to the importance of awareness and prevention, it’s essential to
empower ourselves with knowledge and the tools for living well. PAD can lead to severe complications, yet it is
manageable with early detection and lifestyle adjustments. Throughout this month, we’ll delve into the risk
factors, symptoms, and effective strategies for prevention. Whether you or a loved one is affected, fostering a
supportive community and sharing experiences can significantly enhance quality of life. Join us in spreading
the word, and let’s take significant steps together towards better health and well-being. Together, we can
ensure that Peripheral Artery Disease is recognized and addressed, transforming awareness into action. Let’s
explore how to live well with PAD and enhance our lives in the process.
Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a common circulatory problem in which narrowed arteries reduce blood
flow to your limbs. The arteries supply oxygen to the body and its organs. This condition, often a result of
atherosclerosis, can lead to severe health issues if left untreated. Atherosclerosis is the build-up of fatty deposits
(plaques) in your arteries, which causes them to narrow and harden. When this occurs in the arteries that
supply blood to your limbs, it results in PAD. The reduced blood flow can cause pain, mobility issues, and even
increase the risk of heart attack and stroke, making it a critical health concern that warrants our full attention.
In the early stages, there may be no symptoms.
PAD typically affects the legs, causing symptoms such as leg pain when walking, known as claudication.
Claudication occurs because your muscles aren’t getting enough blood flow to keep up with the demand during
activity. The pain usually disappears after a few minutes of rest. However, as PAD progresses, you might feel leg
pain even when you’re at rest. This condition can also lead to non-healing wounds or ulcers on the feet or toes.
If left untreated, PAD can result in serious complications, including gangrene and amputation.
Understanding PAD is the first step in combating it. Knowledge about the causes, symptoms, and potential
outcomes of PAD can equip individuals with the information they need to seek early intervention. With timely
medical attention and lifestyle changes, many of the complications associated with PAD can be prevented.
Education and awareness play pivotal roles in managing this condition effectively and improving the quality of
life for those affected.
Importance of Peripheral Artery Disease Month
Peripheral Artery Disease Month, observed every September, is a crucial initiative aimed at raising awareness
about this pervasive yet often underdiagnosed condition. The month-long campaign focuses on educating the
public, healthcare professionals, and policymakers about the impact of PAD, emphasizing the importance of
early detection and prevention. By highlighting PAD’s prevalence and potential severity, the initiative seeks to
encourage proactive health measures and facilitate better outcomes for those at risk.
One of the key goals of Peripheral Artery Disease Month is to debunk myths and misconceptions surrounding
the condition. Many people mistakenly believe that PAD is a rare or benign issue, which can lead to delayed
diagnosis and treatment. By providing accurate information and sharing personal stories, the campaign helps
to paint a realistic picture of what living with PAD entails. This increased understanding can prompt
individuals to seek medical advice if they have risk factors or experience symptoms, ultimately leading to
earlier interventions and improved prognosis.
Furthermore, Peripheral Artery Disease Month serves as a platform for advocacy and support. It brings
together patients, caregivers, healthcare providers, and organizations dedicated to fighting PAD. This collective
effort fosters a sense of community and shared purpose, encouraging individuals to take an active role in their
health and support others in their journey. By shining a spotlight on PAD, the campaign aims to reduce the
stigma associated with the condition and promote a culture of empathy and understanding.
Symptoms and Risk Factors of PAD
Recognizing the symptoms and risk factors of Peripheral Artery Disease is crucial for early diagnosis and
intervention. PAD often manifests through a range of symptoms that can vary in intensity and frequency. One
of the most common symptoms is claudication, which is characterized by muscle pain or cramping in the legs
or arms that occurs during physical activity and goes away with rest. This pain typically affects the calves but
can also be felt in the thighs, hips, or buttocks. As the disease progresses, individuals may experience pain even
when at rest, indicating more severe arterial blockage. Many times, these symptoms are usually thought to be
due to arthritis.
Other symptoms of PAD include weakness in the legs and sores or ulcers on the toes, feet, or legs that don’t heal.
Some individuals may notice a change in the color of their legs, such as becoming pale or bluish, and a decrease
in the growth of toenails and leg hair. Erectile dysfunction in men can also be a symptom of PAD. It’s important
to note that not everyone with PAD will exhibit symptoms, which underscores the importance of regular
screenings, particularly for those at higher risk.
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing PAD. Smoking is one of the most significant risk
factors, as it contributes to the narrowing and hardening of the arteries. Other risk factors include diabetes,
high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and a family history of cardiovascular disease. Age is also a factor, with
individuals over 50 being at greater risk. Additionally, people of African descent, those with a sedentary
lifestyle, obesity, or poor dietary habits, are more susceptible to PAD. Understanding these risk factors can help
individuals and healthcare providers prioritize screenings and preventive measures, especially given that in
the early stages, there may be no symptoms at all.
The Role of Awareness in PAD Prevention
Awareness plays a pivotal role in the prevention and management of Peripheral Artery Disease. By educating
the public about the signs, symptoms, and risk factors of PAD, we can encourage individuals to seek medical
advice and adopt healthier lifestyles. Increased awareness can lead to earlier diagnosis, which is critical in
preventing the progression of the disease and reducing the risk of serious complications such as heart attack,
stroke, and limb amputation.
Effective Prevention Strategies for PAD
Preventing Peripheral Artery Disease involves addressing the modifiable risk factors that contribute to its
development. One of the most effective prevention strategies is smoking cessation. Smoking is a major risk
factor for PAD, as it damages the blood vessels and accelerates the progression of atherosclerosis. Quitting
smoking can significantly reduce the risk of developing PAD and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Support groups, counseling, nicotine replacement therapies, medications, and some behavioral interventions
can help individuals quit smoking and maintain a smoke-free lifestyle.
Adopting a healthy diet is another crucial prevention strategy. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains,
lean proteins, and healthy fats can help reduce the risk of PAD by managing cholesterol levels, blood pressure,
and blood sugar. Limiting the intake of saturated fats, trans fats, sodium, and added sugars is essential for
maintaining healthy arteries. Additionally, incorporating foods high in fiber and antioxidants can support
cardiovascular health and reduce inflammation, further protecting against PAD.
Regular physical activity is also vital in preventing PAD. Exercise helps improve blood flow, reduce blood
pressure, and maintain a healthy weight. Aerobic activities, such as walking, cycling, and swimming, are
particularly beneficial for cardiovascular health. Strength training exercises can also help build and maintain
muscle mass, which is important for overall mobility and function. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of
moderate-intensity exercise per week is recommended for optimal health benefits.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage PAD
For individuals diagnosed with Peripheral Artery Disease, making lifestyle changes is essential for managing
the condition and improving quality of life. This is regardless of if interventions such as medications and
procedures are used in the treatment. One of the most important lifestyle adjustments is engaging in regular
physical activity. Exercise can help improve circulation, reduce symptoms, and enhance overall cardiovascular
health. Supervised exercise programs, such as walking regimens, are often recommended for individuals with
PAD. These programs can help increase walking distance and reduce pain associated with claudication.
Dietary modifications are also crucial for managing PAD. A heart-healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits,
vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help control risk factors such as high cholesterol,
high blood pressure, and diabetes. Reducing the intake of saturated fats, trans fats, sodium, and added sugars is
important for maintaining healthy arteries. Additionally, staying hydrated and limiting alcohol consumption
can support overall vascular health.
Managing stress is another important aspect of living well with PAD. Chronic stress can negatively impact
cardiovascular health and exacerbate PAD symptoms. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, deep
breathing exercises, and yoga can help reduce stress and promote relaxation. Engaging in hobbies and
activities that bring joy and fulfillment can also improve mental and emotional well-being. Building a strong
support network of family, friends, and healthcare professionals can provide encouragement and motivation to
maintain a healthy lifestyle.
The Importance of Regular Check-Ups and Screenings
Regular check-ups and screenings are vital for the early detection and management of Peripheral Artery
Disease. Routine medical examinations allow healthcare providers to monitor risk factors, assess symptoms,
and conduct necessary tests to diagnose PAD. Early detection is crucial for preventing the progression of the
disease and reducing the risk of serious complications. Regular check-ups also provide an opportunity for
individuals to discuss any concerns or changes in their health with their healthcare provider.
One of the primary diagnostic tools for PAD is the Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) test. This non-invasive test
compares the blood pressure in the ankle with the blood pressure in the arm to determine how well blood is
flowing. An ABI test can identify blockages or narrowing in the arteries and is often used as an initial screening
tool for PAD. If the ABI test indicates PAD, further diagnostic tests, such as ultrasound, angiography, CAT scan,
or magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), may be conducted to assess the extent of the disease.
Regular screenings are particularly important for individuals with risk factors for PAD, such as smoking,
diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and a family history of cardiovascular disease. Healthcare
providers may recommend more frequent screenings for these individuals to ensure early detection and timely
intervention. By prioritizing regular check-ups and screenings, individuals can take proactive steps to manage
their health and reduce the risk of PAD-related complications.
Resources for PAD Patients and Caregivers
For individuals living with Peripheral Artery Disease and their caregivers, accessing reliable resources and
support is essential for managing the condition and improving quality of life. Numerous organizations and
websites offer valuable information, educational materials, and support services for PAD patients and their
caregivers. These resources can provide guidance on treatment options, lifestyle changes, and coping strategies,
as well as connect individuals with support groups and healthcare professionals.
The Society for Vascular Medicine (SVM), American Heart Association (AHA), and the American College of
Cardiology (ACC) are two prominent organizations that offer extensive resources on PAD. Their websites
feature detailed information on the causes, symptoms, and treatment of PAD, as well as tips for prevention and
management. They also provide tools such as risk assessment calculators, interactive guides, and educational
videos. Additionally, these organizations often host events and webinars focused on PAD awareness and
education.
Support groups and online communities can also be invaluable resources for PAD patients and caregivers.
Connecting with others who are experiencing similar challenges can provide emotional support,
encouragement, and practical advice. Many organizations and hospitals offer in-person and virtual support
groups where individuals can share their experiences and learn from others. Online forums and social media
groups also provide opportunities to connect with a broader community and access a wealth of shared
knowledge and resources.
Success Stories: Living Well with PAD
Hearing success stories from individuals who have managed to live well with Peripheral Artery Disease can be
incredibly inspiring and motivating. These stories highlight the resilience and determination of those who have
faced the challenges of PAD and made positive changes to improve their health and quality of life. By sharing
their experiences, these individuals can provide hope and encouragement to others who are navigating their
own journey with PAD.
One such success story is that of Nathan, a retired teacher who was diagnosed with PAD in his early 60s.
Initially, Nathan experienced severe leg pain that limited his ability to walk and enjoy his favorite activities.
After his diagnosis, he worked closely with his healthcare team to develop a comprehensive management plan.
He quit smoking, adopted a heart-healthy diet, and began participating in a supervised exercise program. With
dedication and support, Nathan’s symptoms improved significantly, allowing him to regain his mobility and
enjoy an active lifestyle.
Another inspiring story is that of Keisha, a professional chef who was diagnosed with PAD after experiencing
persistent foot pain and non-healing ulcers. Keisha’s condition required medical interventions, including
angioplasty to restore blood flow to her legs. Despite the challenges, she remained committed to her health. She
made dietary changes to manage her diabetes and high cholesterol and incorporated regular exercise into her
routine. Keisha also found solace and support in a local PAD support group, where she connected with others
facing similar challenges. Today, she manages her PAD effectively and continues to pursue her passion for
cooking.
Conclusion and Call to Action for Awareness
As we observe Peripheral Artery Disease Month, it is essential to recognize the significance of raising
awareness and promoting prevention strategies. PAD is a serious condition that can lead to severe
complications if left untreated, which extend beyond the legs and involve the heart and brain, but with early
detection and proper management, individuals can live well and maintain a high quality of life. Let us commit
to educating ourselves and others about the symptoms, risk factors, and prevention strategies for PAD. Share
information with family, friends, and colleagues, and encourage them to prioritize regular check-ups and
screenings.