The Future of Regenerative Medicine: Top Benefits of Stem Cells Explained
Regenerative medicine has rapidly evolved from a niche area of scientific research to a promising frontier in healthcare. Central to this revolution is stem cell therapy, a treatment approach that harnesses the body’s own cellular potential to repair, replace, and regenerate damaged tissues and organs. With the increasing prevalence of chronic illnesses and degenerative conditions, understanding the benefits of stem cells is more critical than ever.
Understanding Stem Cells
Stem cells are unique in their ability to develop into different types of cells in the body. Unlike specialized cells, which perform specific functions, stem cells remain undifferentiated, serving as the body’s internal repair system. They can divide and generate new cells, which makes them invaluable for healing damaged tissues. Broadly, stem cells are categorized into:
- Embryonic Stem Cells: Derived from early-stage embryos, these cells have the highest potential for differentiation into any cell type in the body.
- Adult Stem Cells: Found in various tissues such as bone marrow, blood, and fat, these cells are more limited in differentiation but are crucial for tissue repair.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): Adult cells reprogrammed to a pluripotent state, offering similar versatility as embryonic stem cells without the ethical concerns.
The ability of stem cells to transform and multiply underpins many of their therapeutic applications, making them a cornerstone of regenerative medicine.
Also check this: IV NAD therapy
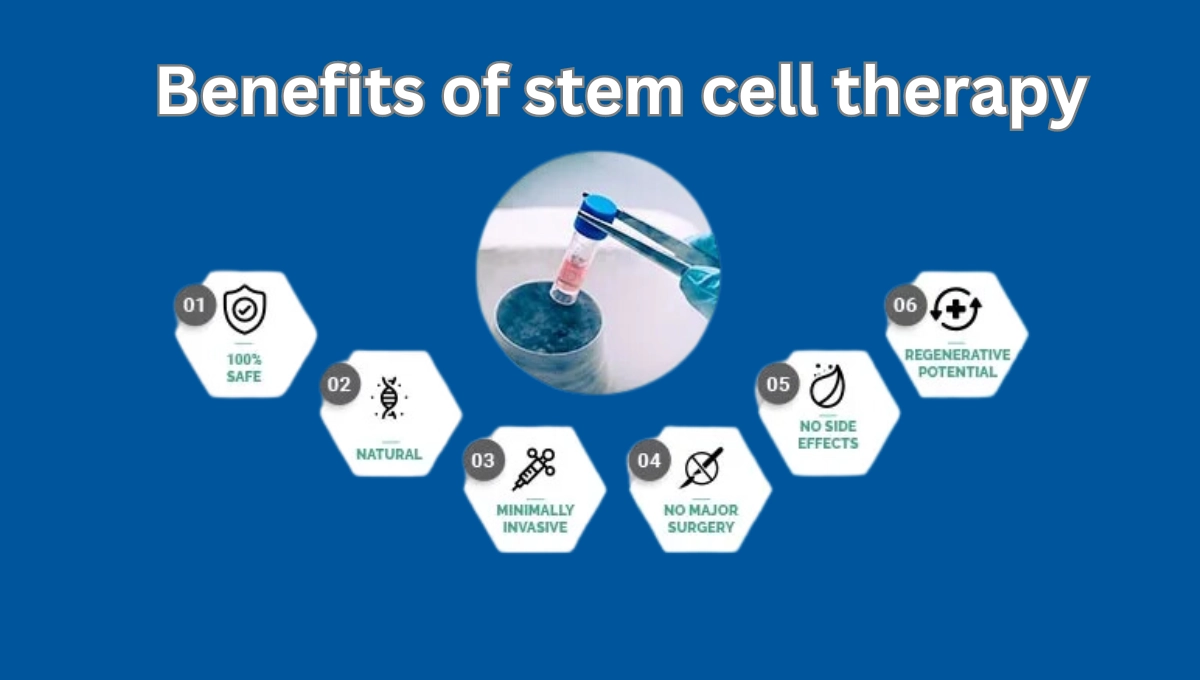
Key Benefits of Stem Cells
The benefits of stem cells extend beyond simple tissue repair; they have transformative potential in treating conditions that were once considered untreatable. Below are the primary advantages that are shaping the future of medicine.
1. Tissue Regeneration and Repair
One of the most significant benefits of stem cells is their capacity to regenerate damaged tissues. Injuries to organs such as the heart, liver, or kidneys often result in permanent damage because these organs have limited natural regenerative capacity. Stem cell therapy offers a solution by promoting the growth of healthy tissue, thereby improving organ function and overall recovery.
For instance, in cardiac patients who have suffered heart attacks, stem cell treatments can help repair scarred heart tissue and restore cardiac performance. Similarly, musculoskeletal injuries like torn ligaments or cartilage degeneration can benefit from targeted stem cell interventions, reducing the need for invasive surgeries.
2. Treatment of Chronic Diseases
Chronic conditions such as diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis have traditionally been managed with medications that alleviate symptoms but do not address the root cause. Stem cells, however, offer a therapeutic approach aimed at the underlying disease mechanisms.
In diabetes, stem cells can be coaxed into insulin-producing cells, potentially reducing or eliminating the need for daily insulin injections. Neurological disorders, including Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s, may see progress as stem cells regenerate neurons and support neural network repair, potentially slowing disease progression.
3. Immune System Modulation
Stem cells also have immunomodulatory properties, meaning they can regulate the immune system’s response. This is particularly beneficial in treating autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. By modulating immune activity, stem cells can reduce inflammation and prevent further tissue damage, offering hope to patients with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or Crohn’s disease.
4. Reduced Dependence on Organ Transplants
Organ shortages remain a critical issue worldwide, with thousands of patients waiting for life-saving transplants. Stem cell therapy could eventually reduce reliance on donor organs by regenerating or repairing failing organs. Research is ongoing into using stem cells to grow functional organ tissues in the lab, which could revolutionize the treatment landscape and save countless lives.
5. Personalized Medicine
Every patient’s condition and biology are unique, and stem cell therapies can be tailored to individual needs. Using a patient’s own stem cells reduces the risk of immune rejection and ensures a more natural integration with the body. This personalized approach not only enhances treatment efficacy but also minimizes potential complications, making therapy safer and more predictable.
6. Accelerated Recovery from Injuries
Athletes and active individuals are increasingly turning to stem cell therapy to enhance recovery from injuries. By stimulating tissue repair at the cellular level, stem cells can accelerate healing times for fractures, tendon injuries, and muscle damage. This approach not only improves the quality of recovery but also reduces the risk of long-term complications associated with conventional treatments.
The Aeon Clinic: Pioneering Stem Cell Treatments
Medical centers like The Aeon Clinic are at the forefront of integrating stem cell research into practical therapies. By combining advanced regenerative techniques with personalized treatment plans, these clinics are demonstrating the tangible benefits of stem cells in real-world applications. Patients with degenerative conditions, chronic illnesses, or sports-related injuries are experiencing outcomes that were once deemed impossible, highlighting the transformative potential of regenerative medicine.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite the remarkable benefits of stem cells, it is essential to acknowledge the challenges and ethical considerations surrounding their use.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Stem cell therapies must pass rigorous clinical trials to ensure safety and efficacy. In some regions, regulations can slow down the availability of innovative treatments.
- Ethical Concerns: Particularly with embryonic stem cells, ethical debates about the source of these cells persist. This has driven the development of iPSCs, which bypass many ethical dilemmas.
- Cost and Accessibility: Advanced stem cell treatments can be expensive and are not yet universally accessible, limiting widespread adoption.
However, ongoing research continues to address these challenges, with promising developments in safer, more cost-effective, and ethically sound treatments.
The Future of Stem Cell Medicine
The trajectory of stem cell therapy points toward a future where regenerative medicine becomes mainstream. Innovations such as gene-edited stem cells, 3D bioprinting of tissues, and combination therapies integrating stem cells with biomaterials are poised to expand the applications of this technology.
In the next decade, we may witness breakthroughs that enable the repair of complex organs, reversal of degenerative diseases, and even enhancement of natural healing processes. As research advances, the benefits of stem cells will likely extend into preventative medicine, chronic disease management, and beyond, fundamentally transforming how healthcare is delivered.
Conclusion
Stem cell therapy represents one of the most promising areas in modern medicine, offering hope to patients with conditions that were once untreatable. The benefits of stem cells—ranging from tissue regeneration and chronic disease management to immune modulation and personalized therapy—highlight their transformative potential. While challenges remain, continued research and clinical advancements are steadily overcoming barriers, making stem cell-based treatments more accessible and effective.
By harnessing the power of these remarkable cells, regenerative medicine is not just healing patients—it is redefining the future of healthcare. Clinics like The Aeon Clinic are leading the way, demonstrating that with innovative therapies, the promise of stem cells is no longer a distant dream but an emerging reality.